Biomass Energy and Biogas in Australia
Most of biomass in Australis is actually biowaste that heads for the landfill. However, biomass could be the future of renewable energy in Australia. In this guide we breakdown what biomass is, how its used to make bioenergy, and the implications this has in Australia's energy future. Read on for this and more.
What is Biomass?
Biomass is a term that is used to refer to organic materials such as plants bacteria, animals and their waste.
Biomass is considered a renewable energy resource as it can be used to create energy through the production of biogas or it can be burned to create energy. The energy created from biomass is called bioenergy.
Biomass is a renewable resource because all living things are biomass and they continually produce biomass as a byproduct of life. A prime example of this is animal waste.
Examples of biomass include:
- Wood & Plant Materials
- Food Waste
- Agricultural & Leftover Crop waste
- Manure
- Organic Municipal Waste (wool, cotton, paper, etc.)
- Sewage
However, biomass on its own is just waste. Therefore, it's also important to understand the significance of biomass in its relation to creating bioenergy.
Need Energy Advice ?
Selectra's Energy Experts are Available To Help You Free of Charge
(Free Selectra Service - Currently open)
What is Bioenergy?
Bioenergy (or biomass energy) is the energy generated from living or once-living organisms. However, fossil fuels are not considered bioenergy.
Up until the late 1800s bioenergy was the main type of energy used on Earth. Bioenergy was often created from burning wood, using it to create charcoal and to boil water to run steam engines.
Nowadays the most common form of bioenergy is biogas.
What is Biogas?Biogas is a byproduct of the decomposition of biomass. Biogas mainly consists of methane and carbon dioxide but can be a mix of many different gasses. Biogas can be used as a form of renewable energy to power our daily lives by using it in traditional combustion engines, gas appliances, or burning it to create electricity.
What is Bioenergy Used For?
Bioenergy has numerous applications for powering daily life.
Here are easy some examples of what bioenergy can be used for:
- Cooking food
- Powering cars
- Heating homes
- Creating more energy
One of the most useful advantages of bioenergy is found in the creation of biogas. An advantage of biogas is that it can easily be stored and transported for use at any time.
Biogas is able to compensate for fluctuations in other renewable energy sources such as in hybrid power plants where it can be difficult or impossible to store wind and solar energy.
Check out other ways to sustainably heat your home such as a solar water heater or a solar pool heater!
Converting Biomass to Bioenergy
We can convert biomass to bioenergy through burning biomass to create energy or decomposing biomass to create biogas. Biomass has the ability to create energy (energy potential) because it has absorbed energy from the sun.
Here's how it works:
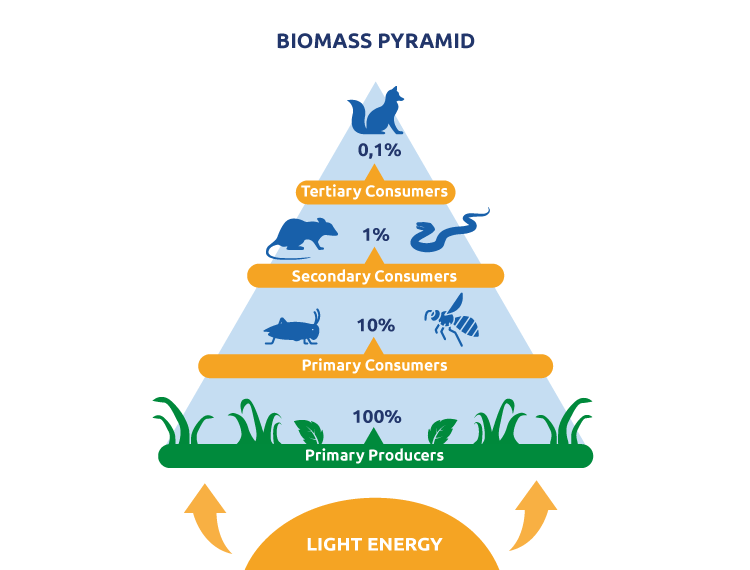
Plants absorb the sun's energy and turn it into physical energy through photosynthesis. Animals eat plants and absorb that energy. Therefore, animal and human waste also contains traces of that energy which can be used to create bioenergy. This transfer of energy is referred to as the biomass pyramid.
Here you can see an image of the biomass pyramid and how energy is transferred from organism to organism.
The most efficient process of biomass to bioenergy is using biomass to create biogas.
As we mentioned before, biogas has high energy potential (meaning it creates lots of energy from a relatively small amount) and has low greenhouse gas emissions making it a very efficient energy source.
Biogas can be used for a number of applications including powering businesses, and heating homes. Another advantage of using biogas to create bioenergy is that this process reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills as waste is the main ingredient in biogas creation.
How is Biogas Made?
Biogas is always made from biomass. Biogas is made from a process called anaerobic digestion.
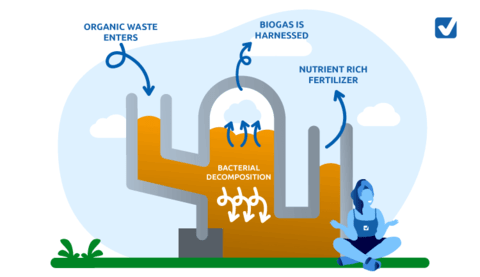
Simply put, the biomass is placed in a tank and all of the oxygen is removed.
Bacteria and other microbes that thrive in oxygen-poor environments aid in the decomposition process and break down the biomass.
Like all living things, the microbes produce waste in the form of gas as they digest the biomass. The gas released by the microbe is called biogas.
How Does Biogas Generate Electricity?
Biogas is not only useful for burning in its gas form. It can also be used to generate electricity.
Biogas can be burned to create electricity through a process called mechanical generation.
Think of your car motor or a home generator. These both work with a combustion engine to spin a mechanical system that generates electricity from its rotations. This method of using biogas to generate electricity is energy efficient, adaptable for existing technology, inexpensive, and readily available.
Theoretically, biogas can be also converted directly into electricity through the use of a fuel cell. However, the high price of fuel cell technology makes it an impractical solution until technology improves.
How to Make Home Biogas Using Biomass
Home biogas can be made in a relatively easily provided you have the right materials. Home biogas is a great source of clean energy and also nutrient-rich fertilizer.
- Here are the steps for creating biogas:
- Remove any inorganic material (such as plastic packaging or glass) from the raw biomass
- Crush the biomass into small pieces (under 10mm) and add liquid to make the biowaste is easier to digest.
- Add microbe cultures
- Heat the biomass to around 37ºc as microbes function best in warm environments.
- Remove oxygen and store the biowaste in a sealed tank for about three weeks.
- The microbes consume the organic material and biogas is formed by the process of anaerobic digestion.
- Remove the biogas from the tank and purify it to remove impurities such as carbon dioxide. This process will make it more flammable and increase its energy potential. The leftover gas will be biomethane.
- There will be leftover solid material in the tank is call digestate. This can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
- Often, the solid and liquid parts of the digestate separate. You can use the liquid digestate to make a slurry for your next biogas project.
How is Biogas Purified?
Unpurified biogas consists of mostly methane and carbon dioxide, with a few other compounds found in small quantities.
For use in existing infrastructure such as gas mains in industrial and residential settings, the biogas must be purified or “upgraded”. Upgrading biogas involves removing the carbon dioxide to make it as close to natural gas as possible and removing hydrogen sulfide to prevent corrosion of metallic parts once the biogas is burnt.
There are a number of methods to upgrade biogas but the most common is through a process called water washing.
Water washing is, quite literally, washing the biogas with water. The biogas is filtered through columns where it is scrubbed by cascading water at a very specific temperature and pressure. Water is very efficient at absorbing carbon dioxide and other unwanted compounds found in raw biogas.
Need Energy Advice ?
Selectra's Energy Experts are Available to Help You Free of Charge
(Free Selectra Service - Currently open)
Bioenergy: Advantages & Disadvantages
Bioenergy is a very underrated resource; it’s not only carbon-neutral but saves organic waste from entering landfills where it would decompose and potentially release toxic liquids into the ground and greenhouse gases into the air.
| Advantages of Biogas | Disadvantages of Biogas |
|---|---|
|
|
Despite these advantages, biomass energy doesn't receive the same public and governmental support as with solar panels, hydropower, or wind power.
Having an equivalent governmental program such as the solar feed-in tariff would help move biomass along. However, there isn’t as much time, energy, research, or money being invested into biogas research despite its potential to help Australia reach its renewable energy target sooner than other methods.
Green Power Want to invest in biogas & bioenergy but don’t have a provider nearby? Green Power is a government-led initiative with Australian companies to allow anyone to invest and commit energy providers to use more renewable energy, for only a few cents per kWh.
Biomass Energy in Australia & the Future of Biogas
Biomass energy and biogas is a small piece of the renewable energy transition in Australia, but one with huge potential.
The latest Clean Energy Report from the Clean Energy Council current lists biogas as one of the smallest sources of clean energy in the country, making up just 5% of Australia's renewable energy profile.
However, the Federal Government’s completion of the national Bioenergy Roadmap might change this. Key points of interest include bio jet fuels & renewable industrial heat generation. The report mentions taking advantage of Australia's agriculture sector as a source of right biomass for conversion to bioenergy.
As the report states, creation of the Bioenergy Roadmap solidifies the “validity and value of the Australian bioenergy industry going forward”. Even in the short time since this roadmap’s development it has already led to a significant increase in the level of interest and development of bioenergy projects in the past year.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as plants, animals, and their waste. It is a renewable resource because it can be continually replenished and used to generate energy through processes like combustion or anaerobic digestion.
How is bioenergy produced from biomass?
Bioenergy is produced by converting biomass into energy through combustion or by creating biogas through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Biogas mainly consists of methane and can be used for electricity, heating, or as fuel.
What are the main applications of bioenergy?
Bioenergy is used for cooking, heating, electricity generation, and powering vehicles. Biogas can be stored and used on-demand, making it a flexible energy source that complements other renewables.
What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy?
Biomass energy is carbon-neutral as it recycles carbon in organic matter. It reduces landfill waste and methane emissions and provides renewable energy independent of weather conditions.
What challenges does biomass energy face in Australia?
Challenges include limited public awareness, less government support compared to other renewables, technical and financial barriers, and sourcing sufficient biomass feedstock sustainably, especially in urban areas.
What is the future outlook for biomass and bioenergy in Australia?
Biomass energy is a small but growing part of Australia's renewable portfolio, supported by government initiatives like the Bioenergy Roadmap aimed at expanding bioenergy projects and reducing emissions with sustainable feedstocks.
More about Renewable

Green Loans for Healthcare Providers: Save on Solar, EVs & Energy

Wind Energy, Wind Turbines, and Wind Power in Australia
Hydroelectricity & Hydropower in Australia

Green Gas: What Is It and Can You Use It at Home?

Green Energy: What It Is and Why It Matters

Smart Lighting Systems in Australia
Click below to find a better deal for your home!